Understanding the Cycle of Product Development for Success
Understanding the Cycle of Product Development for Success
Ideas become real solutions in the dynamic process of design. From the first idea to the last delivery and beyond, it provides a thorough road map for a creation.
Whether you are developing new technology, consumer items, or services, understanding the various stages of production is essential for success in a competitive market.
The product cycle, which serves as a roadmap for businesses to follow from problem identification to market identification, lies at the heart of this process.
Businesses may minimize risks, make well-informed choices, and increase revenues by having a better grasp of the cycle.
By being aware of every phase, from conception to implementation, and knowing how to maximize each one, businesses position themselves for long-term success and sustainable growth.
Looking to build your next big idea? Here’s everything you need to know about Web development services.
What is Product Development?
Product development is the dependent technique of remodeling a concept right into a marketplace-ready answer that addresses specific client wishes or market opportunities.
It involves a chain of steps, consisting of ideation, layout, prototyping, checking out, Developing, and launch, all geared toward developing a product that provides cost to each business and its users.
Defining Product Development
The main components of design are problem-solving and creativity. This is the process of producing or refining content, be it digital apps, services, or tangible goods.
This method ensures that the final product is practical, visually appealing, and financially successful by combining technical know-how, creative thought, and strategic design.
Key Objectives and Goals
Realizing an idea in a way that satisfies consumer demands and complements the organization's strategic objectives is the main purpose of product development.
Delivering solutions that address practical issues, differentiate oneself in a crowded market, and create long-term commercial value are all part of this.
Product development aims to improve customer happiness, foster brand loyalty, and drive innovation to keep the company ahead of market trends in addition to the observable results.
Creating a cycle of Product Development Plan
The key to transforming concepts into profitable goods is a well-designed production process. gives precise instructions, coordinates group activities, and guarantees effective resource usage.
Goals, schedules, and resources must all be carefully considered for effective planning in order to expedite the process from conception to launch.
Steps to Develop an Effective Plan
- Define the Product Vision
Knowing exactly what the product is meant to do is the first step. Give an explanation of its goal, target market, and how it addresses a particular issue or market need. - Conduct Market and Competitor Analysis
Examine consumer preferences, market trends, and rival products. Make use of these observations to improve your product idea and find areas where you can stand out from the competition. - Set Objectives and Milestones
Divide the process of developing a product into manageable stages, each with clear goals and quantifiable benchmarks. This makes it possible to monitor progress and make necessary corrections. - Create a Product Roadmap
Create a broad plan that includes important tasks, deadlines, and dependencies. A thorough roadmap helps stakeholders understand the project and acts as a roadmap for the team for the whole development process. - Plan for Testing and Iteration
Take the time to plan, test, and develop prototypes. Through continual improvement made possible by iterative development, the product is guaranteed to satisfy consumer expectations prior to launch. Discover the smart choice for bringing your vision to life.
Setting Clear Objectives and Milestones
Maintaining content and ensuring that all team members are aware of their tasks depend on setting clear goals. SMART stands for specified, achievable, quantifiable, relevant, and time-certain.
As markers for assessing progress, milestones enable teams to recognize accomplishments and address difficult situations early.
Examples of common milestones that keep the team on track include finishing a prototype, finishing the design, or passing a quality assurance test.
Resource Allocation and Budgeting
Remaining within the budget and assembly deadlines requires effective resource management. Determine the skills, tools, and supplies needed at each level, then distribute resources appropriately.
Make a thorough financial plan that includes expenses for design, enhancement, checkout, marketing, and advertising, as well as any unplanned events.
Monitor aid distribution on a regular basis to make sure it aligns with venture goals, and adapt as necessary to prevent bottlenecks.
Groups may design a strong product development strategy that reduces risks, increases efficiency, and produces goods that meet or beyond expectations by adhering to these guidelines and maintaining polite communication.
Providing companies with Vrutti it solutions.
The Seven Stages of Product Development
Stage 1: Idea Generation
Innovative concepts that address pressing issues in the actual world are the starting point of the creative process.
Understanding client demands and finding market gaps are frequently the first steps in generating successful ideas.
Through examining current solutions and concentrating on client issues, businesses may generate concepts that motivate and provide tangible benefits.
Stage 2: Market Research
Adopting a concept is the next step. Confirming whether your concept fits the demands of your target audience is a crucial task for market research.
Strategies like focus groups, surveys, and competition research provide you information about what your consumers can and will want from your items.
In order to make sure the supply chain satisfies market expectations, this phase helps refine it.
Stage 3: Planning
Strategy is the next stage after gaining an established understanding of the market. This is the stage in which the product roadmap is used.
It's critical to specify objectives, deadlines, and resources required for progress.
All stakeholders' visions and objectives must coincide for the project to proceed successfully, to prevent any obstacles, and to keep everyone in agreement.
Stage 4: Prototyping
The first step in making ideas a reality is creating functional prototypes.
Prototyping is a crucial procedure that enables groups to test concepts, assess implementations, and obtain insightful input.
Through design refinement based on real-world testing, businesses can make sure their product is useful, efficient, and prepared for the next phase.
Stage 5: Sourcing and Development
The focus switches to acquisition and development when the prototype has been tested and refined.
To make sure the product is built to order, it is essential to select the appropriate manufacturers and suppliers.
During this phase, the prototype is turned into a physical, market-ready product, taking manufacturing schedules, pricing, and quality control into account.
Stage 6: Commercialization
The product is now prepared for the market debut. The core of marketing is strategy: organizing how to introduce and market the product to your target market.
Digital campaigns, social media, and conventional advertising are all included in this area, which encompasses methods for creating buzz, increasing awareness, and successfully entering a market.
Stage 7: Post-Launch Improvements
The release is only the beginning of the product's existence in the market, but it may also signal the end of the improvement cycle.
Improvements made after debut are crucial to preserving relevance and guaranteeing sustained pleasure.
Companies may continuously improve the customer experience and stay ahead of the competition by fine-tuning their goods through the collection of user feedback, performance monitoring, and flexibility in response to market changes.
The Structure of a Product Development Team
Well-defined roles and productive teamwork are the foundation of a successful product team.
While upholding high standards, each team member contributes special knowledge to guarantee the final result satisfies client demands and corporate goals.
Core Roles
Product Manager: The Strategic Driver
The product manager manages the overall strategy, establishes the product's direction, and defines its vision. While meeting market requests, setting feature priorities, and overseeing the product roadmap to maintain development momentum, they make sure the final product is in line with the company's goals.
Team Leader: The Delivery Coordinator
The product owner is execution-focused and oversees the product backlog, making sure that activities are well-defined, ranked, and in line with the product's goals. They collaborate closely with the development team and stakeholders to fill in any gaps and maintain an effective and efficient workflow.
Developing Team: The Builders
Through the design, coding, and implementation of technological solutions, the development team makes the product a reality. To guarantee that the product is operational and to resolve any potential technical issues, they work closely with the manufacturer and inspector.
UI/UX Designers: The Experience Creators
Simple, aesthetically pleasing, and user-friendly designs are the responsibility of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) designers. They guarantee that the product offers a distinctive and engaging user experience in addition to fulfilling functional needs.
Quality Assurance (QA) Team: The Gatekeepers
The QA team is important for the quality of the final output. Before the product is delivered, they do thorough testing and feedback to find problems, guarantee functionality, and make sure it satisfies technical requirements and user expectations.
Team Collaboration
Cross-Functional Teams: The Synergy Enablers
A production team's ability to work together is what keeps it together. Different viewpoints are brought together by cross-functional teams, which include representatives from customer service, sales, marketing, and other areas. This methodology promotes smooth communication, enhances problem-solving skills, and yields a comprehensive and marketable output.
Developing teams may be more creative, productive, and produce reliable products that please consumers and improve performance by combining collaborative planning with clearly defined responsibilities.
Best Practices in Product Development
Appropriate processes and procedures are essential to Develop excellence because they guarantee effectiveness and efficiency all along the way.
Adopting agile approaches and improving cross-departmental communication are two best practices that can have a big impact.

Embracing Agile Methodologies
Teams can react rapidly to shifts in client demands, market conditions, and technical advancements thanks to agile methods, which place an emphasis on iterative and continuous development.
Team members can concentrate, make adjustments fast, and guarantee real-time production feedback by segmenting the development process into tiny, manageable sprints.
This method not only expedites time to market but also guarantees that the finished product satisfies consumer demands and corporate goals.
Collaborating Across Departments
The process of developing a product involves teamwork and calls on the knowledge and experience of several departments, including design, developing, marketing, sales, and customer service. Collaboration that works fosters creativity, problem-solving, and a cohesive vision.
Open communication and departmental collaboration help companies spot possible problems early, make decisions more easily, and develop better coordinated action.
Delivering a successful product that is in line with company objectives and customer pleasure is more likely when all the teams are centered around one another from the conception phase to launch and beyond.
Step into the world of mobile development and create the extraordinary future we all deserve.
Common Challenges in the Product Development Cycle
Product development has its share of difficulties, and the path from idea to company is rarely simple. To guarantee a good conclusion, it's critical to recognize and resolve any problems.
Early detection of typical obstacles allows teams to create plans to get over them and keep the process moving forward.
Identifying Potential Pitfalls
Managing unanticipated problems including scope creep, poor market fit, and resource limits is one of the biggest hurdles in product development.
Continuous additions of features or modifications throughout development, known as scope creep, can cause delays and cost excesses.
Inadequate market research might also result in items that don't satisfy consumer preferences or demands.
Product teams also frequently struggle to get the required resources, whether they be technical, human, or financial, or to get stakeholders on board with their aims.
Strategies to Overcome Obstacles
Addressing these issues requires proactive and well-defined efforts. It is possible to avoid what can be done by establishing and adhering to clear, well-defined goals from the start.
Frequent loops and market validation are essential to ensuring the product stays current and fulfills user expectations.
Adapting to changing conditions requires careful planning, adaptability, and priority, according to resource management theory.
Frequent application inspections and open team communication also guarantee that possible problems are found early, addressed, and fixed quickly.
With the correct procedures in place, teams can remain on course and launch their products more quickly.
Conclusion
The product development cycle is a multi-phase process that calls for flexibility, teamwork, and careful planning.
Businesses may overcome obstacles in product development and improve their chances of success by comprehending each step, from ideation to post-launch development.
Using agile approaches and promoting collaboration across departments are important best practices that support teams in adapting and working together, as well as recognizing and resolving shared issues to guarantee the development process runs smoothly.
For upcoming breakthroughs, keep in mind that having a fantastic concept alone won't guarantee product success; execution, continuous learning, and the capacity to adjust to the always shifting market environment are all important.
To realize your goal, maintain your concentration, be innovative, and push forward. The world is constantly anticipating the next great thing—it may be you!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
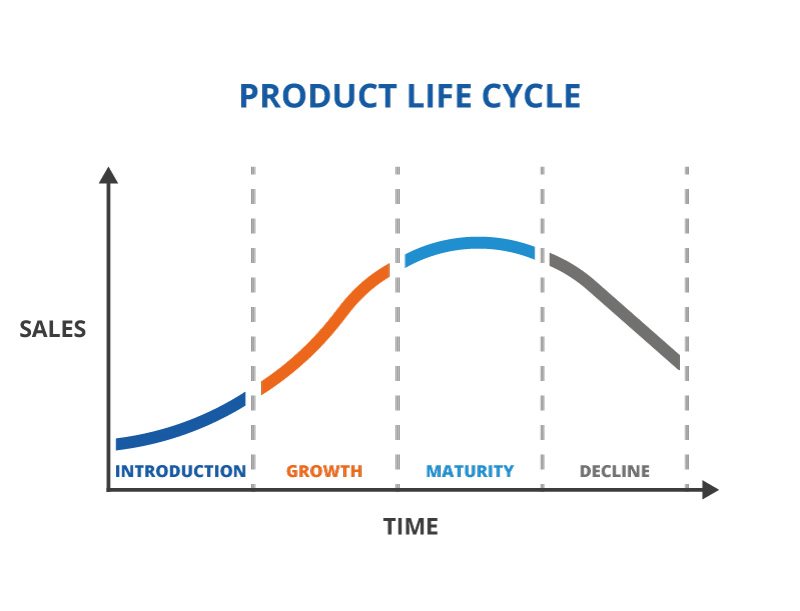
1. Why is Understanding the Product Life Cycle Important?
Businesses may better predict and adjust to shifts in consumer demands, market competitiveness, and market demand by having a solid understanding of the product life cycle. The stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline—allow businesses to prepare strategies for each stage, including resource allocation, pricing, and marketing. Throughout their existence, goods are guaranteed to stay lucrative, competitive, and relevant thanks to this expertise.
2. What’s the Business Case for Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)?
An arranged framework for managing a product from inception to retirement is offered by product lifecycle management, or PLM. PLM's potential to increase productivity, save expenses, and improve product quality makes it a compelling business case. PLM expedites decision-making, reduces time-to-market, and guarantees regulatory compliance by centralizing data and encouraging team cooperation. Additionally, it enables businesses to remain flexible, develop more quickly, and adjust to changing client demands—all of which contribute to long-term success.
3. How to Overcome Common Challenges in Product Development?
A proactive and deliberate strategy is necessary to overcome obstacles in product development:
1. Scope Creep: Prevent it by setting clear project objectives and adhering to them. Regularly review priorities and involve stakeholders in discussions.
2. Resource Constraints: Plan resources meticulously and allocate budgets realistically. Leverage tools for efficient project management and reprioritize tasks when necessary.
3. Market Misalignment: Conduct thorough market research and involve customers in feedback loops to ensure the product aligns with their needs.
4. Cross-Functional Disconnect: Foster collaboration by maintaining open communication channels, hosting regular meetings, and encouraging team alignment on shared goals.
By methodically tackling these obstacles, groups may guarantee a more seamless development process and successful product results.

